Wednesday, August 11, 2021
Team Knowledge Test CBSE
STRUCTURE OF ATOM
ATOM
John Dalton proposed in 1808 that atom is the smallest indivisible particle of matter.
ATOMIC RADII
Atomic radii are of the order of 10–8 cm (1Å) and radii of nuclei are nearly 10–13 cm.
Radius of the nucleus is thus th of the radius of atom.
Radius of atom  Radius of nucleus
Radius of nucleus
ELECTRON
- It was discovered through the study of Cathode rays (discovered by Zulius Plucker) and the name was proposed by Stoney.
- Charge : It was determined by Mullikan by oil drop method as –1.602 × 10–19 coulombs or 4.803 × 10–10 e.s.u.
- Mass : It was found by J. J. Thomson as
9.11 × 10–28 g. - Specific charge : e/m ratio is called specific charge and was determined by Thomson as 1.76 × 108 coulombs/gm.
- Radius : It is of the order 10–15 cm.
- Density : 2.17 × 1017 g/cc.
- Mass of electron at speed v is m =
- Atomic mass unit : It is 0.0005486 amu.
- Mass of one mole of electron : It is 0.55 mg.
CATHODE RAYS
Originate from cathode. Electrons were discovered by cathode ray experiment.
SOME PROPERTIES OF CATHODE RAYS
- They cast shadow of the object in their path
- Rotate a mica wheel
- Deflected by electric and magnetic fields in a direction showing negative charge.
PROTON (H+)
Discovered by Goldstein (1886) through perforated cathode rays experiment which showed the presence of anode or canal rays.
- Mass : It was found to be 1.672 × 10–24 g or 1.672 × 10–27 kg or 1.00728 amu. It is about 1837 times heavier than an electron.
- Charge : It carries unit positive charge 1.602 × 10–19 coulombs or 4.803 × 10–10 esu.
- Specific charge : It is 9.58 × 104 coulomb/gm. It varies with nature of gas and is maximum if H2 is used.
- Charge on 1 mole of proton is 96500 coulomb or 1 Faraday.
- Volume : The volume for proton is approximately 1.5 × 10–38 cm3.
NEUTRON (0N1)
Discovered by Chadwick by bombarding Be or B atoms (sheet) with high speed 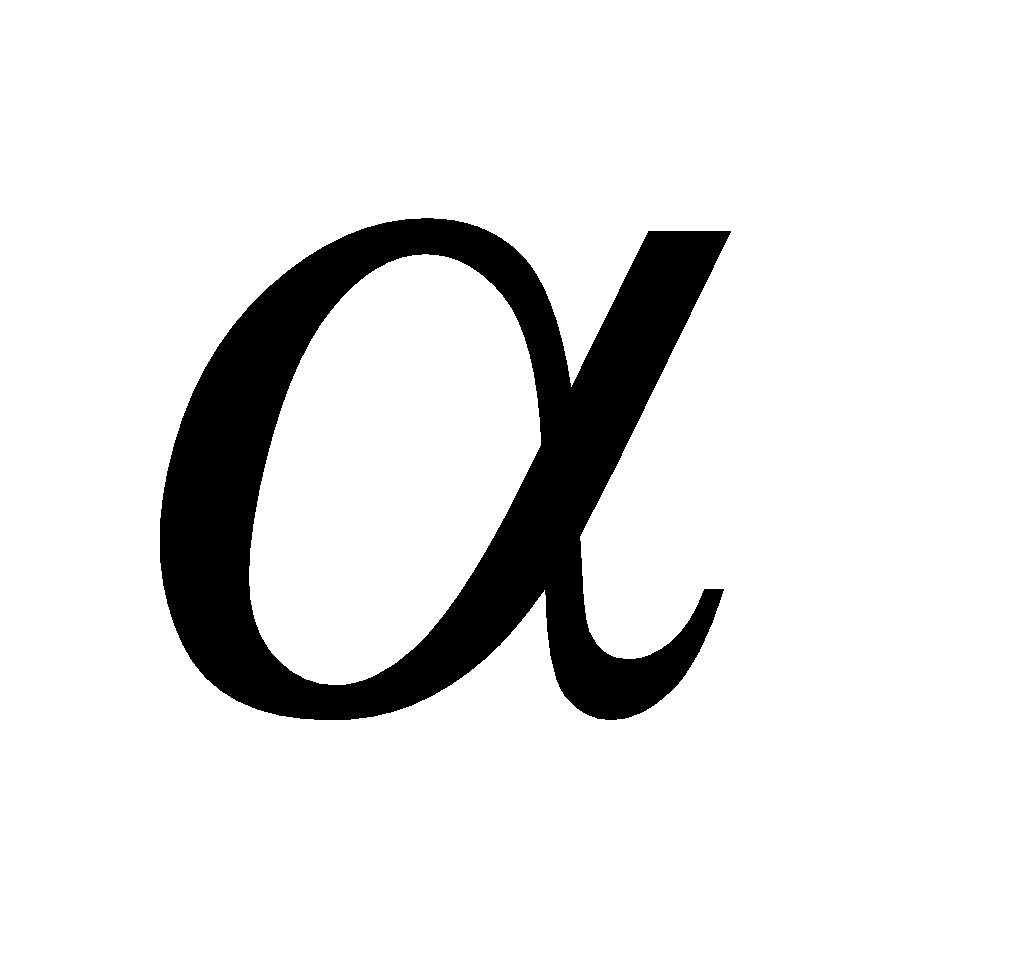 -particles
-particles
- Mass : Its mass is 1.675 × 10–24 gm or 1.675 × 10–27 kg or 1.00866 amu.
- It is heavier than proton by 0.18%.
- Density : Its density is 1.5 × 1014 g/cm3.
- Specific Charge : It is zero.
- Stability : It is least stable of all elementary particles present in an atom.
- Disintegration : Isolated neutron is unstable and disintegrates into electron, proton and neutrino.
- Among all elementary particles neutron is the heaviest and least stable.
OTHER SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
- Positron (Positive electron +1e0). Discovered by Dirac (1930) and C. D. Anderson (1932). They are highly unstable and produce
-rays on combining with electrons.
- Neutrino and Antineutrino are particles of small mass and no charge as stated by Fermi (1934). Anti-neutrino spin clockwise and neutrino spin anticlockwise.
- Meson : They are unstable particles and include pions (
+,
– or
0) Kaons (K+, K–, K0, K–0) and eta meson (
).
Mass : They have mass intermediate of electron and proton.
Discovery : By Yukawa (1935) and Kemmer.
- Anti proton (–1p1) : Negative proton produced by Segre and Weigland (1955) by proton-proton and proton-neutron collisions.
- v-particles : They may be positive, negative or neutral. Discovered by G. D. Rochester and C C. Butler v– and v0 are 2200 times heavier than electron. Heavier disintegrate into pions and lighter into mesons.
THOMSON'S ATOMIC MODEL
Atom is a sphere of positive electricity with a number of electrons distributed within the sphere.
RUTHERFORD'S NUCLEAR MODEL
It is based upon  -particles scattering experiment. Only a few (one in 10,000)
-particles scattering experiment. Only a few (one in 10,000)  -particles were returned back from the Au-foil (10–4 mm thick).
-particles were returned back from the Au-foil (10–4 mm thick).
Conclusion - Atom consists of two parts - (a) Nucleus (b) Extra nuclear part.
Drawbacks - Model fails to explain the stability of the atoms and line spectrum of hydrogen.
NUCLEUS
- Nucleus : It is small heavy and positively charged material located in the centre of atom and electrons are distributed in extra nuclear part of atom and revolve around the nucleus.
- Radius : It is of the order 1.5 × 10–13 cm to
6.5 × 10–13 cm (1.5 – 6.5 Fermi). In general
Where r0 is a proportionality constant with value 1.4 × 10–13 cm. and A is mass number.
- Volume : It is about 10–39 cm3. and that of atom is 10–24 cm3
- Density : It is about 1014 g/cm3.
- Diameter : It is about 10–15 m or 1 fm (1 fm = 10–15 m)
- Nucleus contains neutrons and protons, collectively known as nucleons.
ATOMIC NUMBER/MOSELEY'S POSTULATES
The number of protons present in an atom is called the atomic number, denoted by Z. Moseley postulated that the frequency of X-rays produced when beam of strong electrons fall on metal target, called anti-cathode is related to the charge present on the nucleus of an atom of the element used as anti cathode. Mathematically
MASS NUMBER
It is sum of number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus (nucleons as a whole) and denoted by A. It is always a whole number.
AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS
It is the average mass of all existing isotopes and not necessarily a whole number.
ISOTOPES
Isotopes are atoms of the same element having same atomic number but different mass number. e.g. 8O16, 8O17 and 8O18. They were discovered by Soddy (1911).
ISOBARS
Atoms of different elements having same mass number but different atomic numbers e.g. 19K40, 20Ca40.
ISOTONES
Atoms of different elements with different atomic and mass numbers but same number of neutrons e.g. 14Si30, 15P31, 16S32.
ISODIAPHERS
Atoms having same Isotopic number.
ISOELECTRONIC SPECIES
Species having same number of electrons e.g. CO and CN– (both contain 14 electrons each) Na+ and Ne (both contain 10 electrons each).
The ionic size decreases with increasing effective nuclear charge of iso-electronic species.
Ionic size of isoelectronic species depend on 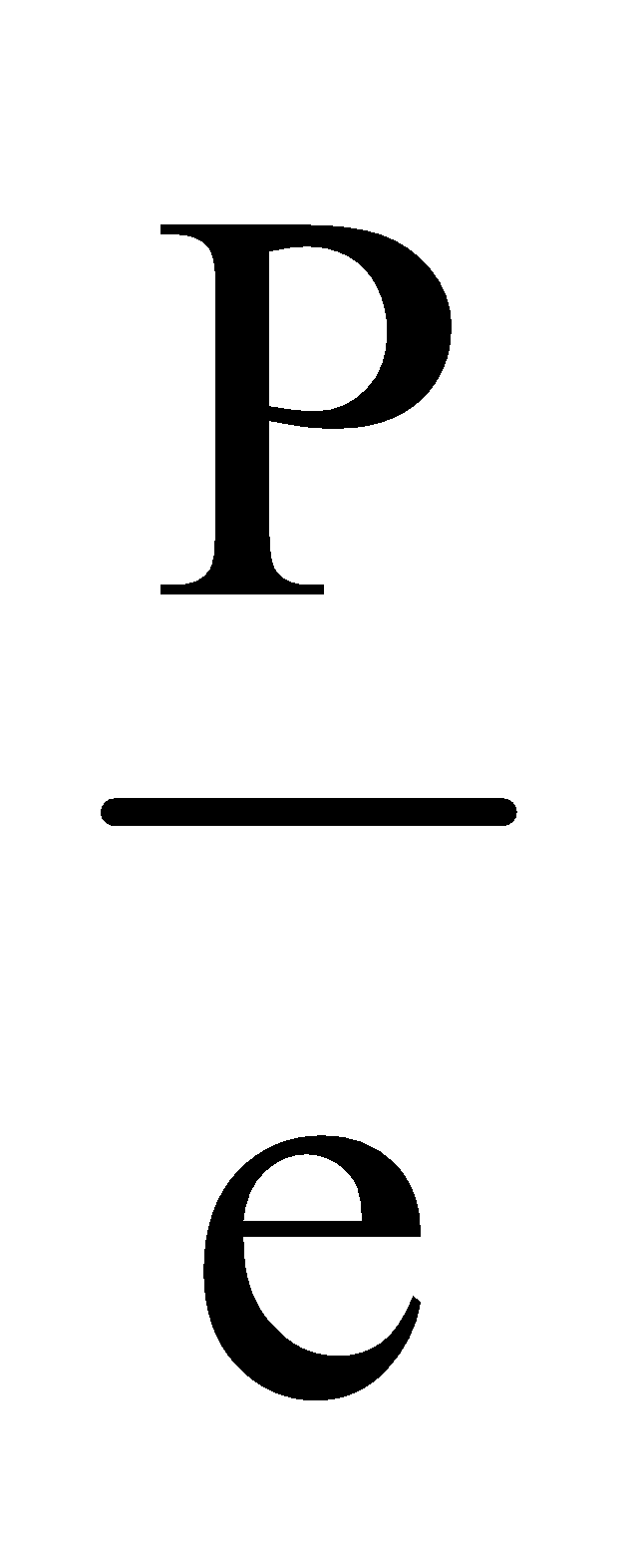 (effective nuclear charge).
(effective nuclear charge).
Ionic size 
Species C4– N3– O2– 
Nuclear Charge 6 7 8 9
Total electrons 10 10 10 10
Ionic Radius (Å) 2.60 1.70 1.40 1.36
Species Na+ Mg2+ Al3+ Si4+
Nuclear Charge 11 12 13 14
Total electrons 10 10 10 10
Nuclear charge) 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4
Ionic radius (Å) 0.95 0.65 0.50 0.41
FAILURE OF RUTHERFORD'S MODEL
According to classical theory of electromagnetism whenever a charge is subjected to an acceleration around an opposite charge, it emits radiations continuously. Therefore the electron while moving around nucleus in circular path must lose energy, go into spiral motion and ultimately fall into the nucleus. Practically it does not happen.
PLANCK QUANTUM THEORY
According to Max Planck (1901) radiant energy is emitted or absorbed only in discrete units in form of bundle or packets of energy called photon (quantum). Photon is not a material body. It is massless bundle of energy
Energy associated with each photon (quantum) :
E = h =h
=h 
E = h
h = Planck's constant = 6.626 × 10–34 Js in S.I. units
(or 6.6726 × 10–27 ergs in c.g.s. units).
(or 6.6726 × 10–27 ergs in c.g.s. units).
c = velocity of light,
Thus, a body can radiate energy in multiples of quantum h , 2h
, 2h , 3h
, 3h .... nh
.... nh where n is an integer.
where n is an integer.
INTENSITY OF LIGHT
It is defined as number of photons falling per unit area per sec. and depends upon wavelength of photons.
or
It is defined as amount of energy falling per unit area per sec and depends upon wavelength of photons.
ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
Electromagnetic radiation by James maxwell (1870). An electrically charged particles moving under acceleration produces alternating electrical and magnetic fields mutually perpendicular to each other. These fields are transmitted in the form of waves having same wavelengths, frequency, speed and amplitude and are called electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiations. In vacuum all types of electromagnetic radiations travel at the same speed (3.0 × 108 ms–1) regardless of wavelengths.
WAVELENGTH
It is the distance between two neighbouring crests or troughs of wave.
FREQUENCY
It is the number of waves which pass through a particular point in one second. Unit is Hertz (Hz) or cycles per second. 1 Cps = 1 Hz.
VELOCITY
It is the distance travelled by wave in one second. Unit is
m sec–1 and denoted by c.
m sec–1 and denoted by c.
c =  .
.
WAVE NUMBER
It is the number of wavelengths per cm. It is equal to the inverse of wavelength. Unit is cm–1 and is denoted by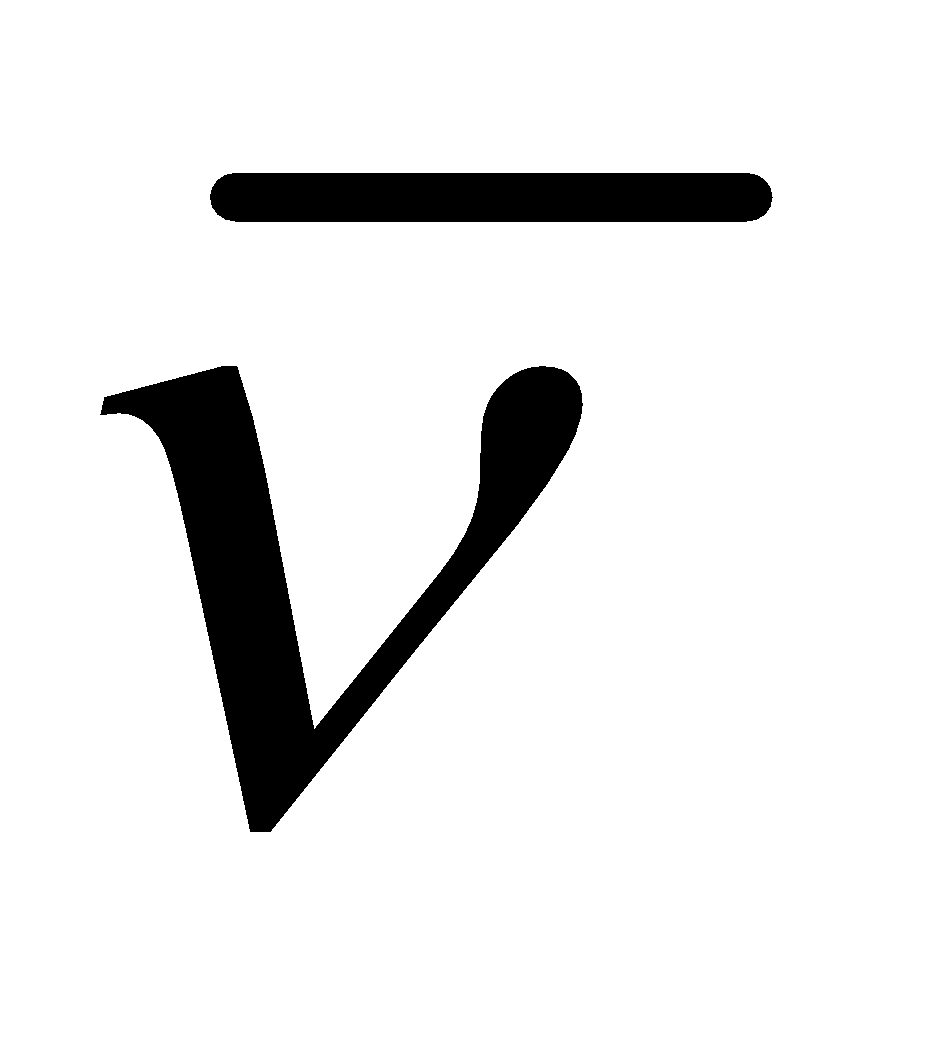 .
.
AMPLITUDE
It is the height of crest or trough. Square of amplitude determines the amount of energy carried by the wave.
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
Arrangement of all electromagnetic radiations in the increasing order of their wavelengths or decreasing order of frequencies is called electromagnetic spectrum.
Rays Wavelength ( in Å) Frequency (
in Å) Frequency ( in Hz)
in Hz)
Cosmic Rays 3×1021 to infinity
X Rays 1.0 2×1016 to 3×1019
UV Rays 150 7.9×1014 to 2×1016
Visible Light 3800 3.9×1014 to 7.9×1014
Infra Red 7600 1×1011 to 3.95×1014
Micro Waves 6×106 1×109 to 5×1011
Radio Waves 3×109 1×105 to 1×109
ATOMIC SPECTRUM
Atoms of different elements emit electromagnetic radiations of definite frequencies when excited by heating, passing current or electric discharge. Arrangement of these radiations in decreasing order of frequencies is called atomic spectrum.
DISPERSION
Phenomenon of splitting of beam of light into radiations of different frequencies after passing through a prism is called dispersion.
CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM
It is obtained by passing sunlight (white light) through a prism. The light is dispersed or resolved into continuous spectra of colours from Violet to Red. It contains radiations of all the frequencies.
LINE SPECTRUM
It is an atomic spectrum of an element which consists of a number of bright lines separated by dark bands. Atomic Spectra of most elements is line spectrum.
ABSORPTION SPECTRUM
It is obtained by passing white light through solutions or vapours of chemical substance and then is analysed by spectroscope. It has few dark lines in otherwise continuous spectrum.
EMISSION SPECTRUM
It is obtained by passing radiations from the atoms through prism. It has few bright lines against a dark background.
HYDROGEN SPECTRUM
It is obtained by passing light being emitted from discharge tube containing hydrogen at low pressure through spectrograph.
Hydrogen Spectrum has five Series
Spectral Line Region n1 n2
Lyman Series U.V. 1 2, 3, 4.....
Balmer Series Visible 2 3, 4, 5.....
Paschen Series I.R. 3 4, 5, 6.....
Brackett Series I.R. 4 5, 6, 7....
Pfund Series I.R. 5 6, 7, 8....
Wavelength of line in spectrum is given by the expression
RH = Rydberg Constant, Z = charge on nucleus,
n1, n2 = electronic levels involved in transition, = Wave number
= Wave number
n1, n2 = electronic levels involved in transition,
also for hydrogen where  is frequency.
is frequency.
- For calculation of longest wavelength line use n2 nearest and for shortest wavelength line use n2 infinity e.g. value of longest wavelength in Balmer Series of hydrogen spectrum use n1 = 2 and n2 = 3.
- Last line of spectrum is called Series limit. Last line is the line of shortest wavelength and high energy when n2 = we get last wavelength
- Number of Lines in a Transition : Mathematical formula for number of lines is follows as
No. of lines = 
BLACK BODY RADIATION
The radiation emitted by a body when heated is called black body radiation. The frequency of radiation increases with temperature. At a given temperature the intensity of radiation emitted increases with decrease of wavelength, reaches a maximum value and then starts decreasing with further decrease of wavelength. A black body can emit and absorb all frequencies.
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
Phenomenon of ejection of electrons from the surface of a metal when light of suitable frequency strikes on it is called photoelectric effect.
- Threshold frequency (v0) : The minimum frequency of incident radiation to cause the photoelectric effect is called threshold frequency.
- Work function : A part of the photons energy that is absorbed by the metal surface to release the electron is known as work function of the surface denoted by
. The remaining part of the energy of photons goes into the Kinetic energy of the electron emitted.
If  0 is the threshold frequency and
0 is the threshold frequency and  the frequency of incident light then
the frequency of incident light then  and E = h
and E = h .
.
Note:
- K.E. is independent of the intensity of light.
- Number of photoelectrons Intensity of light
- K.E. is directly proportional to frequency of incident light.
is known as Einstein's photoelectric equation.
- Energy required to stop the ejection of electrons is given by eV0 where e is the electric charge and V0 is stopping potential.
BOHR’S MODEL OF ATOM
Proposed by Niel Bohr to overcome the drawbacks of Rutherford’s model.
- Electrons revolve around nucleus only in certain selected circular orbits. These orbits are associated with definite energies and are called energy shells or levels.
- Electrons can move only in those circular orbits where angular momentum is a whole number and multiple of h/2
. i.e. mvr =.
or simply an integral number of wavelengths should fit in given electron orbit of radius r i.e. n
=2
r.
- Electrons energy in a particular orbit is constant.
- Lowest energy state is called ground state and when electron absorbs energy and jumps to higher state, it is called excited state
- Electronic energy is negative because at infinite distance there is no interaction between electron and nucleus thus energy is zero. While when close to nucleus, attraction takes place, energy is released and it becomes negative as it was already zero. The energy of electron increases with the value of n, but the difference of energy between two successive orbits decreases. Thus
E2 – E1 > E3 – E2 > E4 – E3 .......... etc.
- Energy of electron in nth orbit
where m = Mass of the electron,
e = Charge on the electron,
h = Planck's constant
n = Principal quantum number,
k = A universal constant = 9.0 × 109 J.m/C2
The constant k is inverse of permitivity factor 4
 0 of the medium . The numerical value of permitivity factor is 4
0 of the medium . The numerical value of permitivity factor is 4
 0 = 1.11264 × 10–10 C2N–1m–2. In C.G.S. system k = 1.
0 = 1.11264 × 10–10 C2N–1m–2. In C.G.S. system k = 1.
- Radius of nth orbit
rn =  Å
Å
- Velocity of electron in nth orbit,
The velocity of electron in first orbit of hydrogen is  of the velocity of light.
of the velocity of light.
- Kinetic energy of electron in nth orbit,
- Potential energy of electron in nth orbit,
- Total energy of electron in nth orbit,
- Number of revolutions per second in nth orbit,
- Angular velocity
- Angular momentum = mvr
- Number of spectral lines when electron jumps from the nth to ground level =
- The electrons energy is generally expressed in kcal or kJ mol–1 or in electron volts eV.
1 erg mol–1 = 1.44×1013 kcal mol–1 = 6.022×1013 kJ mol–1
1eV = 1.602×10–19J
- Some important values :
In c.g.s. system,
m = 9.109×10–28g
e = 4.803×10–10 esu,
h = 6.626×10–27 ergs,
k = 1
RH 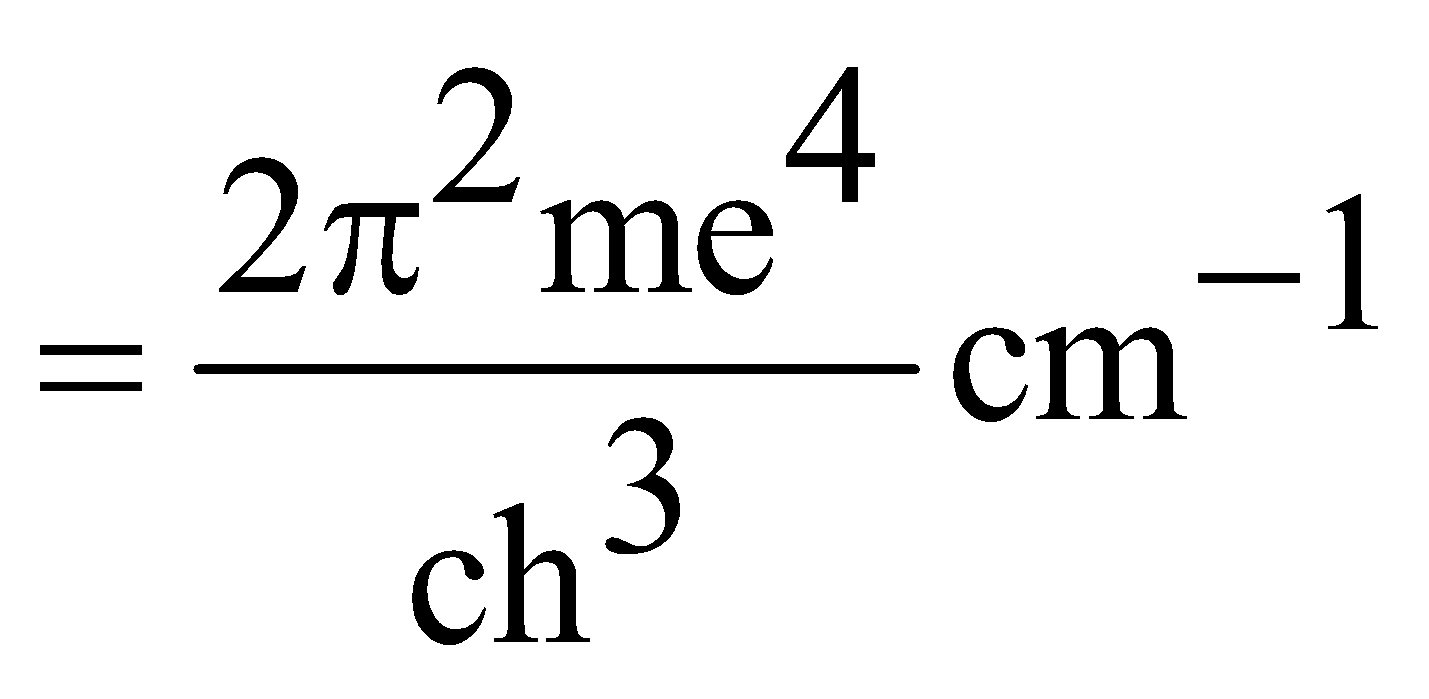
In S I system,
m = 9.109×10–31kg
e = 1.602×10–19C,
h = 6.626×10–34 J.s,
k = 9.0 × 109 Jm/C2
RH = 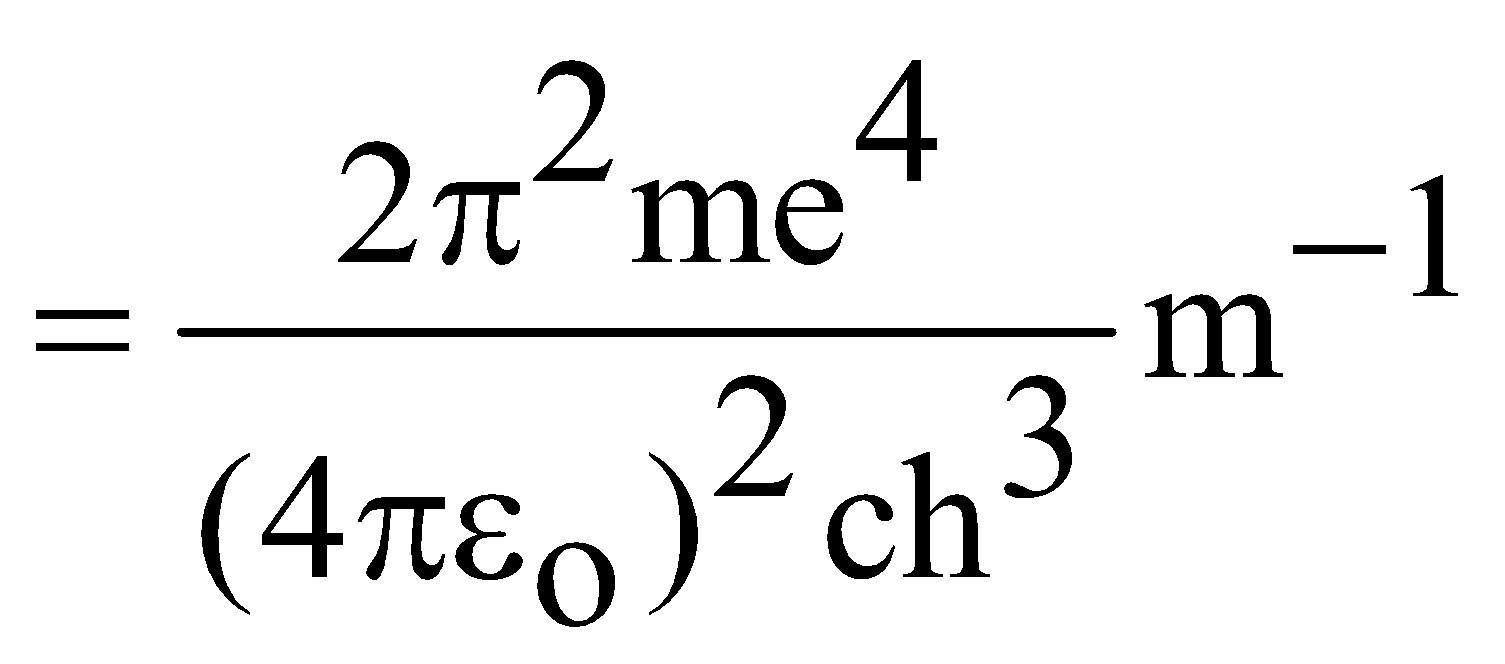
In SI system the charge e is replaced by 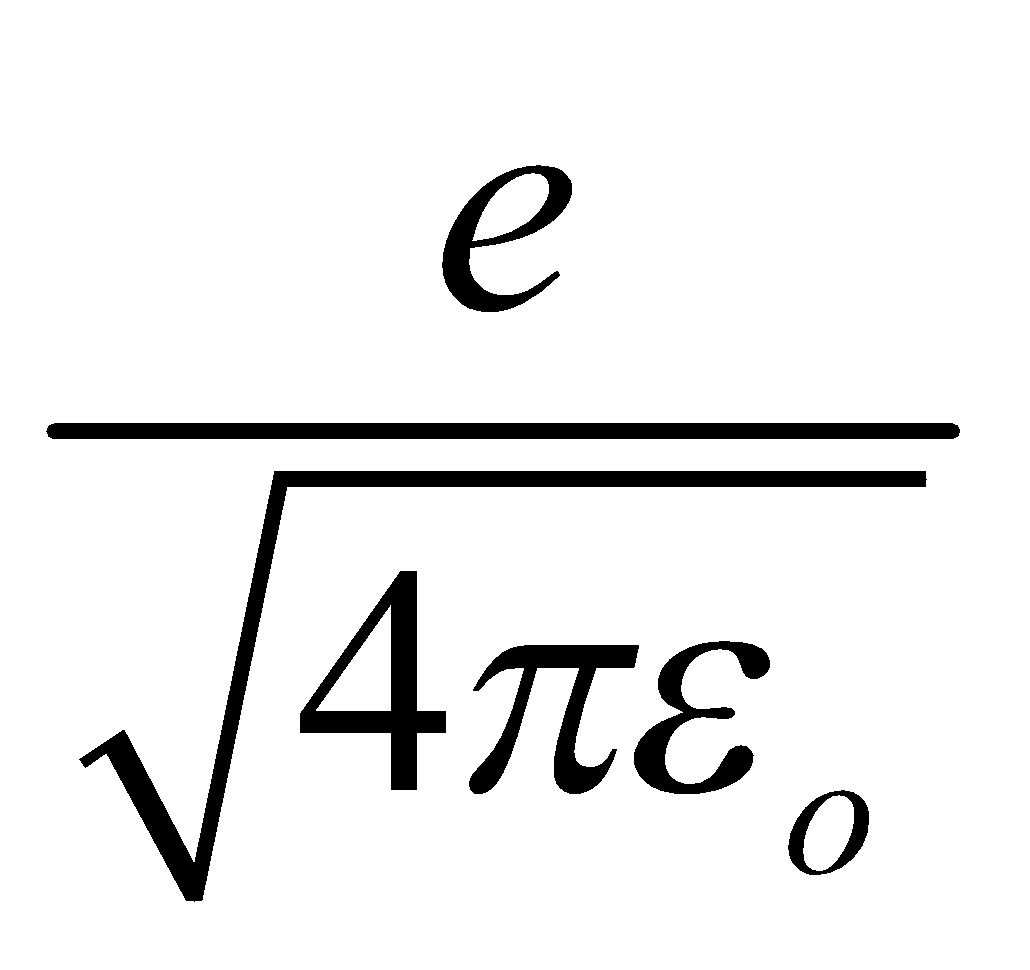
LIMITATIONS OF BOHR’S MODEL
- Explains the spectrum of elements having only one electron
- Does not explain splitting of spectral lines under magnetic field (Zeeman effect) and electric field (stark effect)
- Does not explain quantisation of angular momentum.
- It goes against the Heisenberg’s uncertainity principle.
SOMMERFIELD MODEL
- Motion of electrons is in closed elliptical paths of definite energy levels having nucleus on either of the focii.
- Angular momentum is quantized
where k = 1, 2 ---------n.
- It does not explain distribution of electrons in extranuclear part of atom and also does not explain for de Broglie concept.
QUANTUM MECHANICS
It was developed independently by Warner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrodinges and takes into account the dual behaviour (particle and wave nature) of matter proposed by de Broglie.
Planck’s Quantum theory successfully explains.
- Photoelectric effect
- Black-body radiation
- Line spectra of H-atom
- Variation of heat capacity of solids with temperature.
DE- BROGLIE PRINCIPLE (1924)
- Proposes that just as radiations have particle nature, the material particles are also associated with wave nature.
- de Broglie wavelength is h =
Planck’s constant m = mass of object ; v= velocity and this equation is called the de Broglie equation.
DAVISSON AND GERMER’S EXPERIMENT
Confirms the wave nature of electrons.
SCINTILLATION METHOD AND PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
Confirm the particle nature.
HEISENBERG’S UNCERTAINITY PRINCIPLE
“It is not possible to determine simultaneously the position and momentum of small moving sub-atomic e.g., particle , such as electron with entire certainty”.
, such as electron with entire certainty”.
- Mathematically
where, x = uncertainity in position 

- As the mass of particle increases, the uncertainity decreases
QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL OF ATOM
- Based on de Broglie's and Heisenberg’s principle.
- Put forward by Schrodinger (1920). Behaviour of electron was described in terms of equation known as Schrodinger wave equation
- Many solutions for this equation are possible for hydrogen but only certain solutions are permissible and are called eigen values
- The solution must be single valued, should satisfy the relation
and must be finite and continuous.
has no physical significance but
gives intensity of electrons and thus gives probability of electron in a particular region.
ORBITALS
Orbitals are the regions in space around nucleus where probability of finding the electron is maximum.
- Probability does not become zero even at infinity and is given by
.
- Electron orbitals in atoms are called atomic orbitals while those in molecules are called molecular orbitals.
- Orbitals have definite energy and momentum and are quantized. i.e, En = –E1/n2 thus Bohr’s concept of well defined orbits is ruled out.
QUANTUM NUMBERS
- Four quantum numbers (n, l, m, s) help in providing complete information about an electron in an atom.
- Principal quantum number (n) determines the energy and average distance of electron. It has whole number values also denoted as K, L, M, N. etc. As n increases, distance of electron from nucleus increases and energy increases.
- Azimuthal quantum number (l) determines angular momentum of the electron. It also determines the shape of orbitals and it may have all possible whole number values from 0 to n–1 for each principal energy level. The sublevels are:
Value of l 0 1 2 3
Sub-shell s p d f
Magnitude of angular momentum of an electron in orbital, mvr = 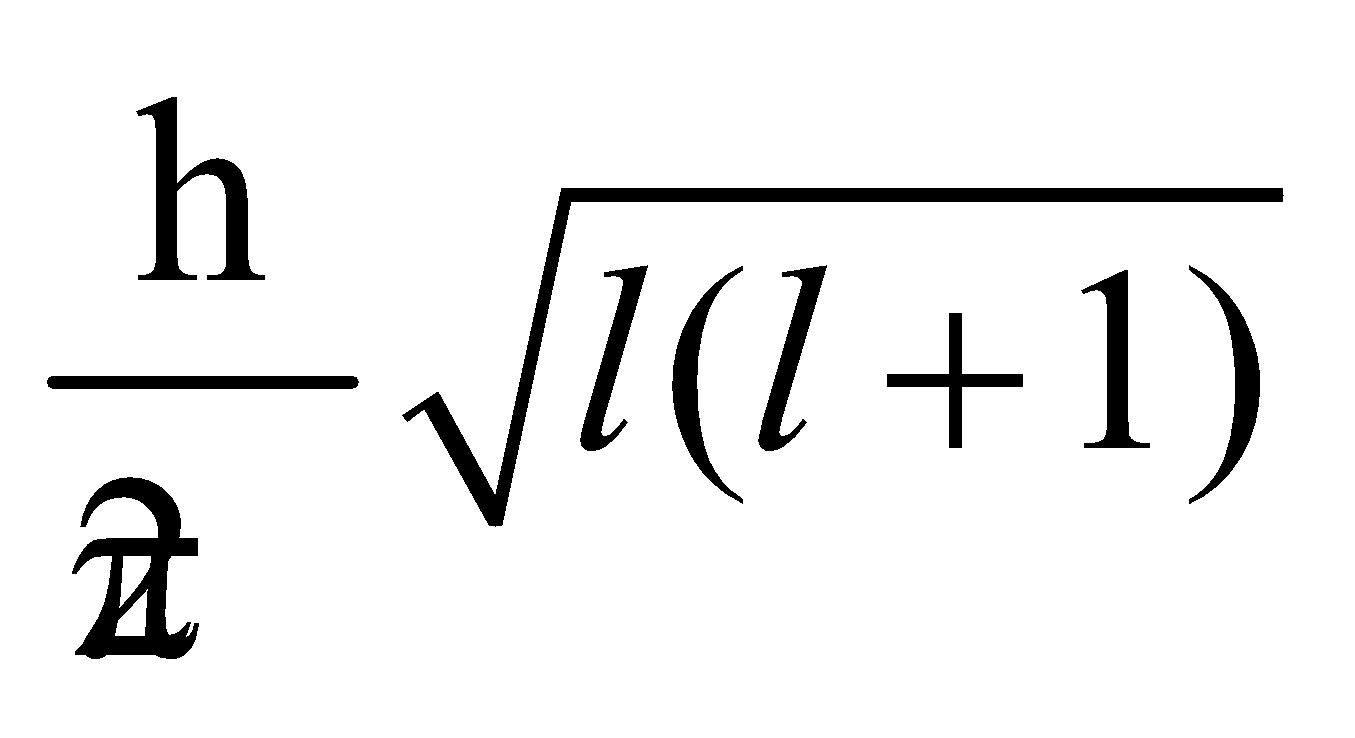
Angular momentum of an electron in any orbit,
mvr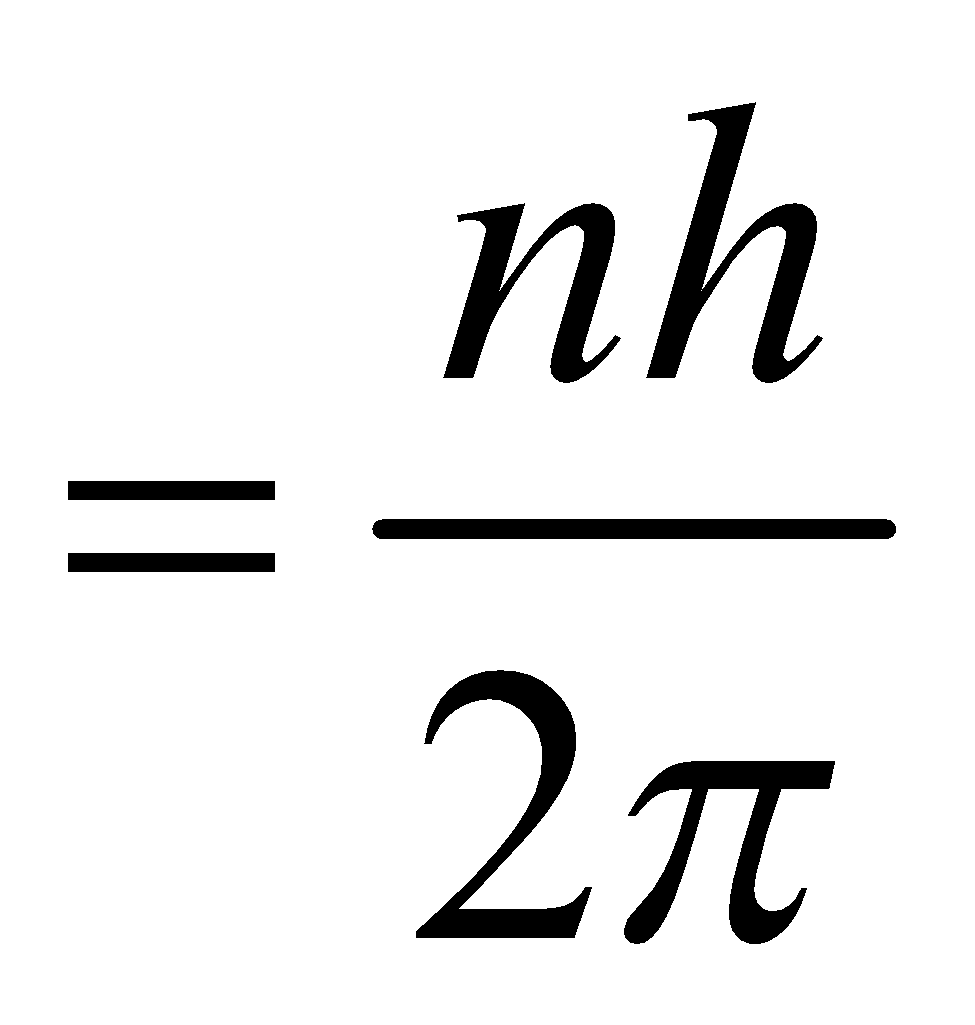
mvr
- Magnetic quantum number (m) defines the orientation of electrons cloud in a particular sub shell. Values of m are the number of orbitals associated with a particular sub shell in main shell. Values of m lie from 0 to l. Total values of ‘m’ for a given n is n2. Total values of ‘m’ for a given l is 2l +1. The table shows a clear relation between quantum numbers.
Shell (n) Sub -shells (l) Orbitals (m)
n=1K shell l= 0
shell l= 0 1s m = 0
1s m = 0
n=2L shell l= 0
shell l= 0 2s m = 0
2s m = 0
l= 1 2p m = –1,0, +1
2p m = –1,0, +1
n=3 M shell l= 0
M shell l= 0  3s m = 0
3s m = 0
l= 1  3p m = –1, 0, +1
3p m = –1, 0, +1
l= 2  3d m = –2, –1, 0,+1, +2
3d m = –2, –1, 0,+1, +2
- Spin quantum number (s) tells the spin of the electron. It can have two value
(clockwise) and
(anticlockwise). Mathematically
where s is amplitude of spin quantum angular momentum.
SHAPE OF ORBITALS
- s orbitals are spherically symmetrical.
- p orbitals are dumbbell shaped.
- d orbitals have five different orientation. Three of them dxy, dyz, dxz are identical in shape but have different orientation.
- The plane passing through nucleus where probability of finding the electron is zero is called a nodal plane. Number of nodal planes in an orbital = l. Number of nodal planes increases with increasing value of n. e.g. 1s has no nodal plane. 2s has one nodal plane. For e.g. : s orbitals (l=0) have no nodal plane, p orbital (l=1) have one nodal plane, d orbitals (l=2) have two nodal planes.
Nodal plane = n-l-1
- Orbitals of a sub shell having same energy are called degenerated orbitals.
- Spherical surface within an orbital where probability of finding an electron is zero is called spherical or radial node. Number of spherical nodes = (n–l–1). Angular or non spherical nodes = (l). Thus total nodes = (n – 1).
Shape of s-orbital :
Shape of p-orbital :
for 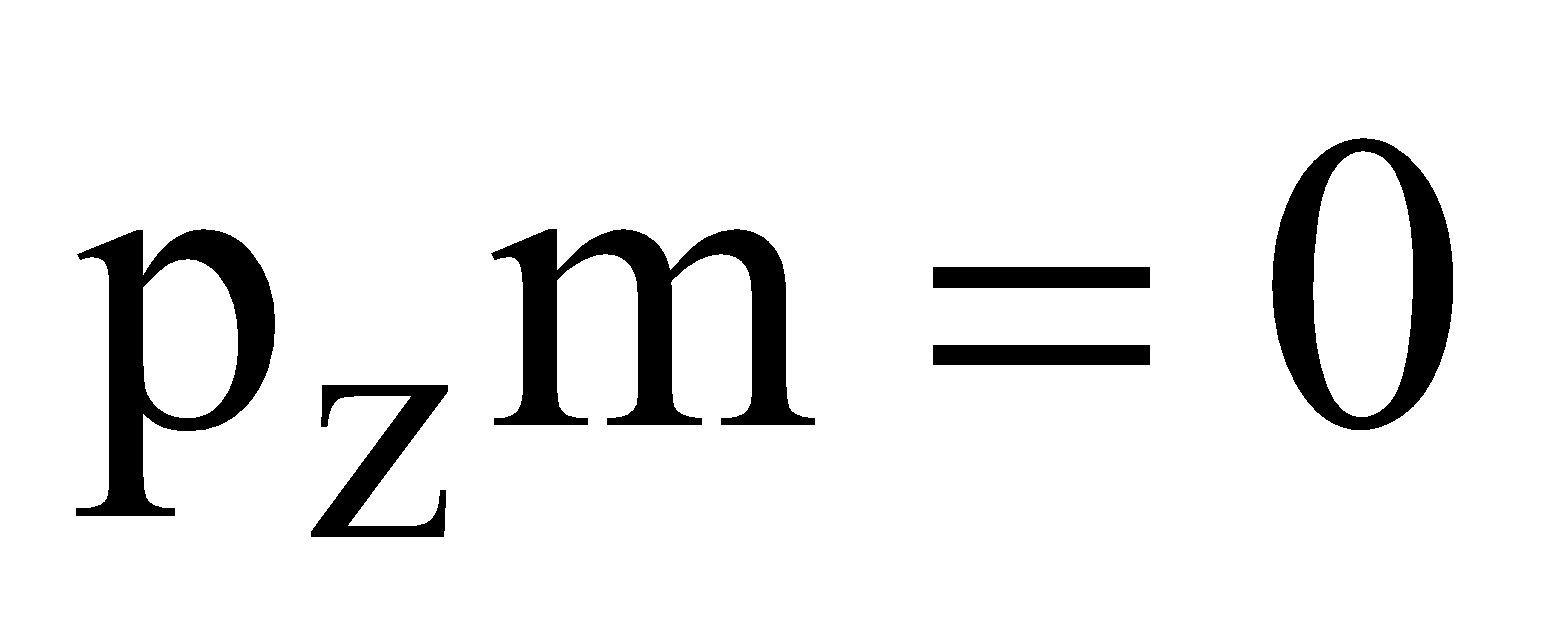 and for
and for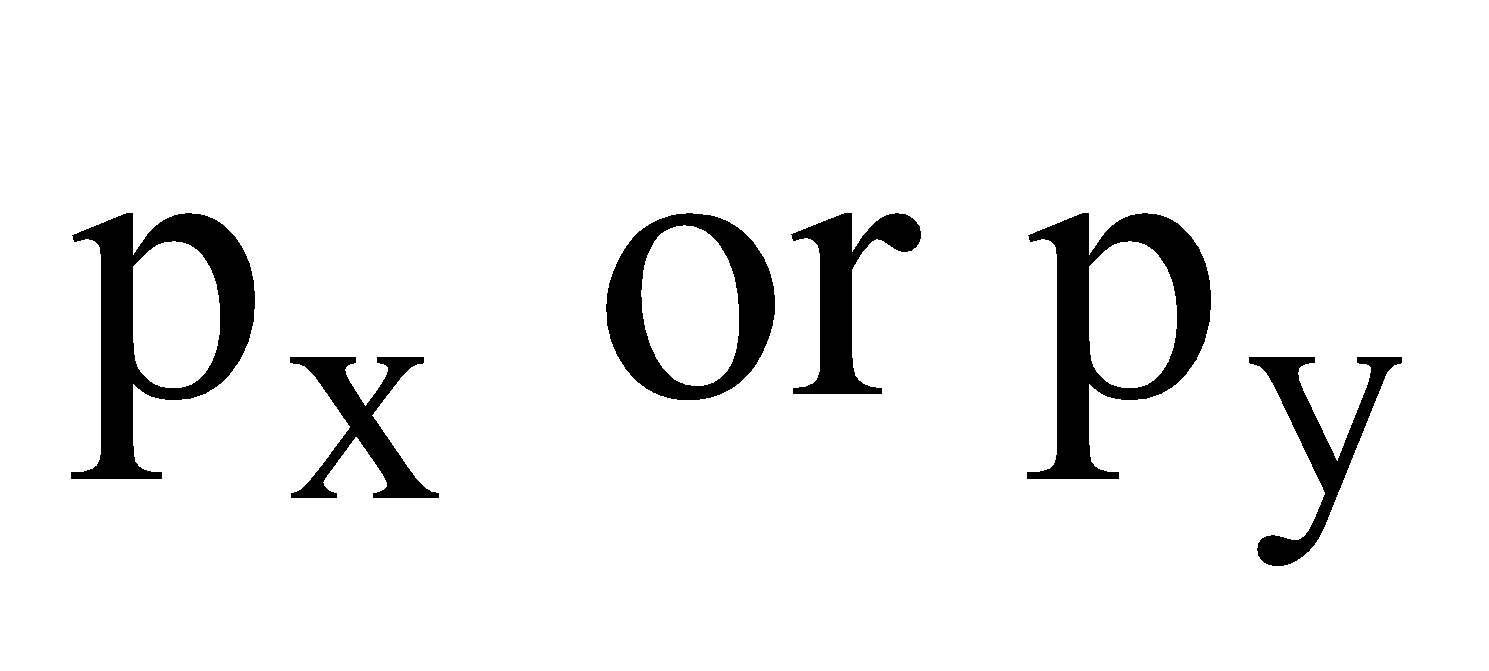 ,
, 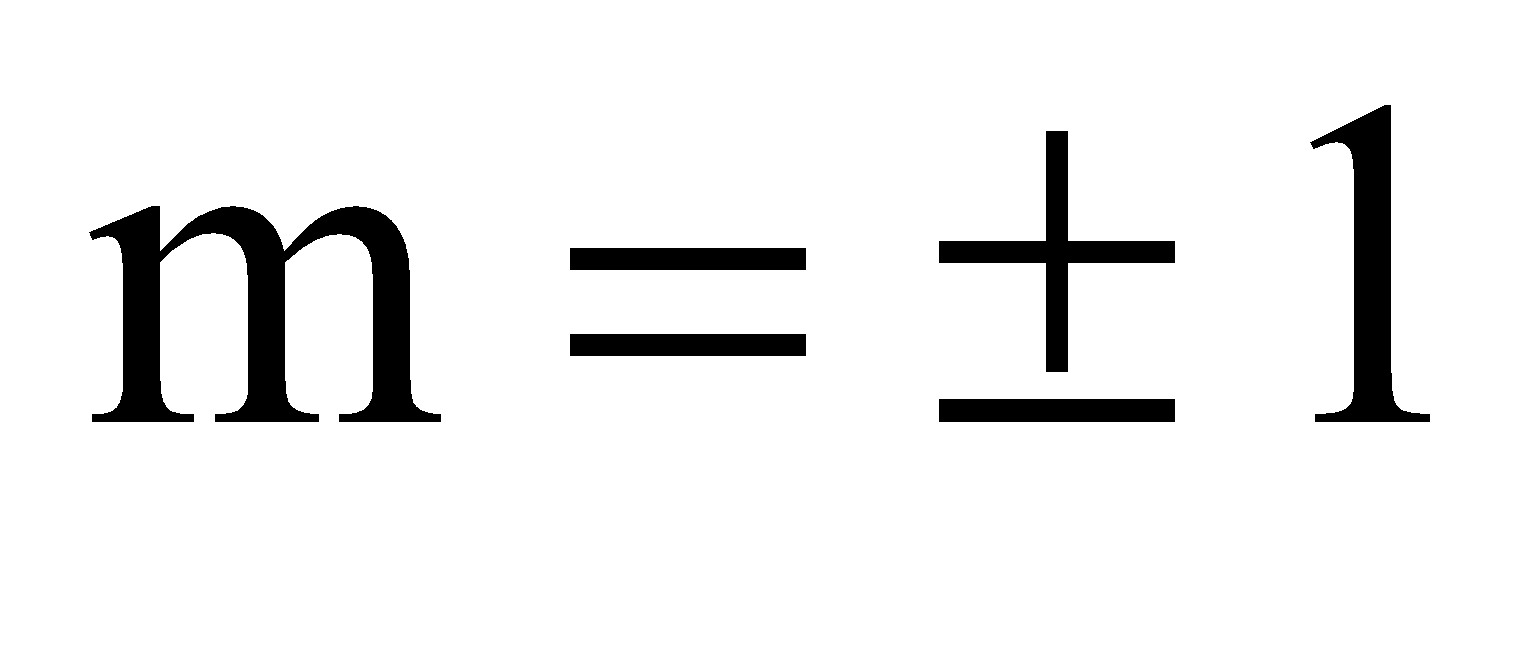
Shape of d-orbitals :
PAULI’S EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE
No two electrons in an atom can have same values for all the four quantum numbers.
- It is not possible to accomodate more than two electrons in an orbital. In other words. s sub shell can have maximum of 2 electrons p sub shell can have maximum of 6 electrons. Thus max. no. of electrons in a shell can be 2n2.
- Maximum number of electrons in a sub shell can be 2, 6, 10, 14 in s, p, d, f respectively and max. electrons in an atomic orbital can be 2.
Maximum number of electrons in a sub shell is equal to 
where 
Note : Maximum numbers of electrons in an orbital = 2
AUFBAU’S RULE
Electrons are added to orbitals in increasing order of energies. The order of energies for orbitals is 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s.
- The order of energies can be calculated by (n + l) rule. i.e. orbitals are filled in order of increasing (n+l) values the one with lower n value is filled first.
- The energy of atomic orbitals for H-atom depends on the value of n only.
1s < 2s = 2p < 3s = 3p = 3d < 4s = 4p = 4d = 4f
HUND’S RULE OF MAXIMUM MULTIPLICITY
The pairing of electrons in orbitals of a subshell does not take place until all orbitals of sub shell are singly occupied.
- This arrangement leads to lower energy level.
- Singly occupied orbitals should have same spins giving rise to lower energies.
RADIAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION CURVES
The electron density is directly proportional to  . The larger the value of
. The larger the value of  more is the probability of finding the electrons. Schrodinger wave equation may be separated into a product of three functions dependent on
more is the probability of finding the electrons. Schrodinger wave equation may be separated into a product of three functions dependent on 
R (r) = Radial wave function, it may be 0, or
R2 = Radial density in per unit volume of spherical shell.
It is always positive.
Note : 
 is the volume of spherical shell having small thickness dr.
is the volume of spherical shell having small thickness dr.
In case of s orbitals the number of peaks is equal to n,
In case of p orbitals the number of peaks is equal to (n–1),
In case of d, orbitals the number of peaks is equal to (n–2)
The point at which the probability of finding the electrons is zero is called nodal point.
The distance of maximum probability increases with increase in the value of n. hence 2s, 2p electrons are greater distance than 1s. and have greater energy also.
ANGULAR PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION CURVES
The total angular  (
( ).
). (
( ) depends only on the direction and remain independent of the distance electrons from the nucleus
) depends only on the direction and remain independent of the distance electrons from the nucleus
Angular probability distribution curves for s and p orbitals. The length of the line OP is proportional to the probability of finding the electrons. The length of the line OP is the same in all directions for s orbital Hence there are equal chances for finding electrons in all directions from the nucleus.
The length of line decreases with increasing in the value of angle
RITZ. COMBINATION PRINCIPLE
It states that the wave number 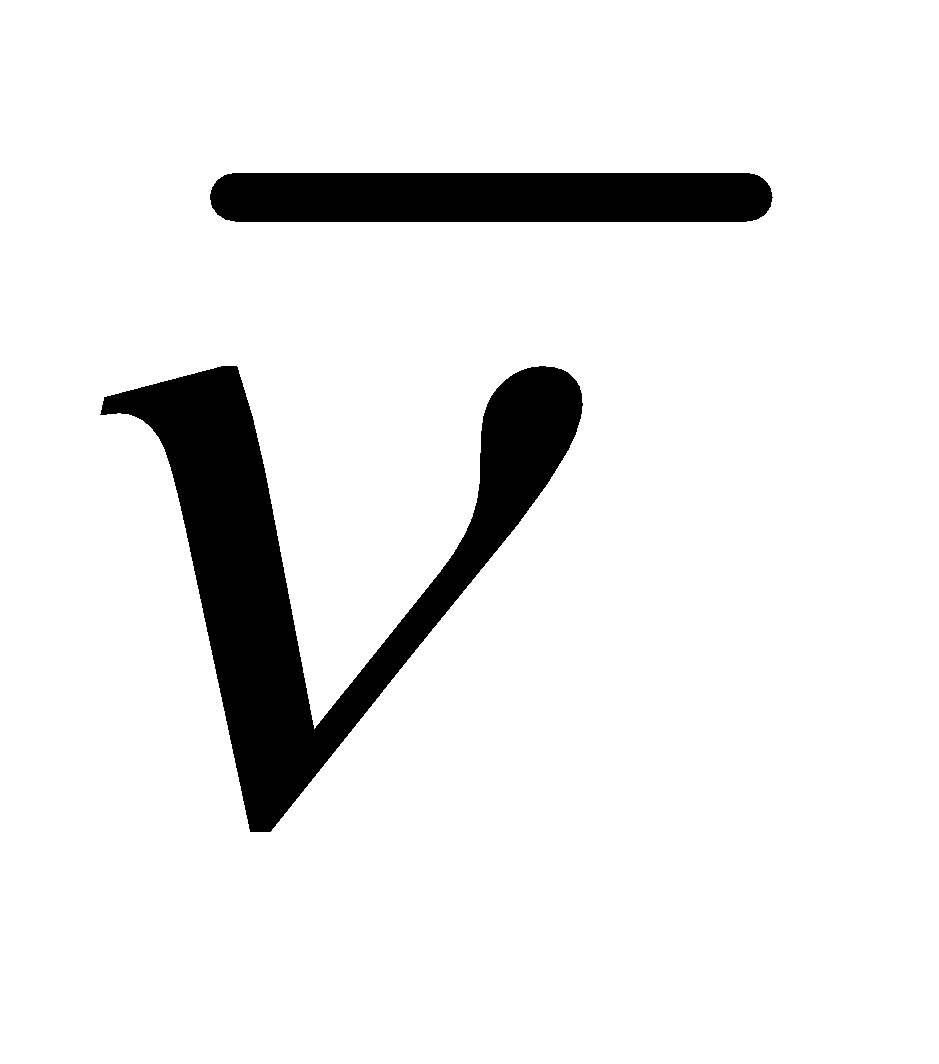 (reciprocal of wavelength) of any line in hydrogen spectrum of a particular series can be represented as a difference of two terms, one of which is constant and other varies throughout the series. Mathematically, .
(reciprocal of wavelength) of any line in hydrogen spectrum of a particular series can be represented as a difference of two terms, one of which is constant and other varies throughout the series. Mathematically, .
RH = Rydberg constant
COMPTON EFFECT
The decrease in energy (or increase in wavelength) of X-rays after the scattering from the surface of carbon or light element is known as Compton effect.
Tags:
structure of atom class 11
structure of atom class 9
structure of atom hindi
structure of atom class 11 solutions
structure of atom class 11 pdf
structure of atom ppt
structure of atom class 11 handwritten notes
structure of atom class 9 pdf
structure of atom all formulas
structure of atom animation
structure of atom and molecule
structure of atom assertion and reason
structure of atom and nuclei
structure of atom and chemical bonding
structure of atom assignment
structure of atom activity
structure of atom byju's
structure of atom book
structure of atom by arvind arora
structure of atom by physics wallah
structure of atom book pdf
structure of atom by unacademy
structure of atom by rutherford
structure of atom basic concepts
structure of atom class 9 notes
structure of atom class 11 notes for neet
structure of atom diagram
structure of atom discovered by
structure of atom definition
structure of atom drawing
structure of atom deleted portion
structure of atom dpp
structure of atom detailed notes
structure of atoms don't memorise
structure of atom exercise
structure of atom extra questions
structure of atom explanation
structure of atom extra questions class 11
structure of atom electron configuration
structure of atom exam fear
structure of atom exemplar class 11
structure of atom exercise class 9
structure of atom formula
structure of atom full chapter
structure of atom for neet
structure of atom for class 9
structure of atom formula sheet for neet
structure of atom for class 8
structure of atom for class 7
structure of atom full chapter class 11
structure of atom gif
structure of atom grade 11
structure of atom given by
structure of atom gneet
structure of atom grade 7
structure of atom grade 11 notes
structure of atom grade 9
structure of atom grade 11 ppt
structure of atom handwritten notes
structure of atom hydrogen
structure of atom history
structure of atom hsslive notes
structure of atom hd images
structure of atom in hindi
structure of atom important questions
structure of atom is organic or inorganic
structure of atom in hindi pdf
structure of atom images
structure of atom is studied in which branch of chemistry
structure of atom introduction
structure of atom important questions class 11
structure of atom jee questions
structure of atom jee notes
structure of atom jee
structure of atom jee advanced questions
structure of atom jee mains
structure of atom jee advanced
structure of atom khan academy
structure of atom kcet questions
structure of atom keam questions
structure of atom lesson
structure of atom lesson plan
structure of atom learn cbse
structure of atom learnohub
structure of atom lesson pdf
structure of atom labeled
structure of atom mcq
structure of atom meaning in hindi
structure of atom mcq class 11
structure of atom model
structure of atom mcq for neet
structure of atom molecule and chemical bond
structure of atom mind map
structure of atom mcq pdf
structure of atom notes
structure of atom ncert
structure of atom notes class 11 pdf
structure of atom neet questions
structure of atom neet notes
structure of atom ncert solutions
structure of atom neet notes pdf download
structure of atom neet questions pdf
structure of atom one shot
structure of atom objective questions
structure of atom online test
structure of atom of hydrogen
structure of atom of oxygen
structure of atom of carbon
structure of atom of class 11th
structure of atom of helium
structure of atom pdf
structure of atom pdf class 11
structure of atom ppt class 11
structure of atom previous year questions neet
structure of atom pdf class 9
structure of atom ppt class 9
structure of atom physics wallah
structure of atom questions
structure of atom question answer
structure of atom questions for neet
structure of atom questions class 11
structure of atom quiz
structure of atom questions class 9
structure of atom quantum numbers
structure of atom quiz class 11
structure of atom revision notes
structure of atom rutherford
structure of atom revision notes neet
structure of atom solutions
structure of atom slideshare
structure of atom short notes
structure of atom short notes class 11
structure of atom summary
structure of atom short notes for neet
structure of atom shells
structure of atom scientist
structure of atom test
structure of atom topics
structure of atom test class 11
structure of atom textbook
structure of atom table
structure of atom timeline
structure of atom theories
structure of atom tricks
the structure of atom
the structure of atom class 9
the structure of atom class 11
the structure of atom class 9 notes
the structure of atom class 8
the structure of atom pdf
the structure of atom class 9 pdf
the structure of atom class 9 mcq
structure of atom unacademy
structure of atom upsc
structure of atom under electron microscope
structure of atom unacademy neet
structure of atom video
structure of atom vedantu
structure of atom valency
structure of atom vedantu class 11
structure of atom video class 11
structure of atom vedantu neet
structure of atom weightage in neet
structure of atom wikipedia
structure of atom was discovered by
structure of atom worksheet
structure of atom with orbitals
structure of atom was given by
structure of atom with diagram
structure of atom with label
structure of atom youtube
structure of atom 11 notes
structure of atom 11th
structure of atom 11th ncert
structure of atom 11 ppt
structure of atom 11th ncert solutions
structure of atom 10th class notes
structure of atom 10th class
structure of atom 10th class ssc
structure of atom 3d
structure of atom 3d model
structure of atom 3d animation
structure of atom 9th class
structure of atom 9th ncert
structure of atom 9th class notes
structure of atom 9 class notes
structure of atom
class 11 chemistry notes
cbse class 11
cbse class 11 notes
class 11 maths
class 11 physics
atomic model
class 11 chemistry
class 11 physics notes
ncert class 11 maths
the nucleus of an atom contains
structure of atom class 9
nucleus of an atom
class 11 english
class 11 chemistry chapter 1
ncert class 11 chemistry
class 11 english chapter 1
class 11 chemistry chapter 1 notes
structure of atom class 11 notes
structure of atom class 11
class 11 biology notes
class 11 biology
ncert class 11 physics
class 11 biology ncert
the nucleus of an atom consists of
states of matter class 11
class 11 maths chapter 1
structure of atom class 9 notes
class 11 chemistry chapter 2 notes
class 11 physics chapter 1
states of matter class 11 notes
class 11 physics chapter 2 notes
chemical bonding class 11 notes
redox reaction class 11 notes
atomic structure notes
nucleus of an atom contains
fluorine lewis dot structure
describe the structure of an atom
class 11 biology chapter 1 notes
class 11 chemistry handwritten notes pdf
class 11 maths notes
informatics practices class 11
thermodynamics class 11 notes
organic chemistry class 11 notes
ncert exemplar class 11 maths
class 11 physics chapter 1 notes
atomic structure of oxygen
class 9 science chapter 4
class 11 biology chapters
ncert exemplar class 11 biology
p block elements class 11
atomic structure of sodium
class 11 chemistry chapter 3 notes
mycbseguide class 11
atomic structure of hydrogen
atomic structure of carbon
structure of water molecule
electron dot structure of chlorine
class 11 biology chapter 1
hydrocarbons class 11 notes
ccp lattice
ncert exemplar class 11 chemistry
ncert solutions for class 9 science chapter 4
ch 11 maths class 10
business studies class 11 chapter 1
equilibrium class 11 notes
thermodynamics class 11 chemistry
my cbse guide class 11
class 11 maths chapter 9
class 11 physics chapter 3 notes
vedantu class 11
class 11 physics chapter 2
ncert exemplar class 11 physics
class 11 biology handwritten notes pdf
hydrogen class 11 notes
chapter 2 chemistry class 11
class 11 maths chapter 10
class 11 chemistry chapter 2
class 11 business studies chapter 1
s block elements class 11 notes
rutherford model of atom class 11
class 11 maths chapter 2
class 11 biology notes pdf
electronic structure of sodium
p block elements class 11 notes
in a solid ab having nacl structure
electronic structure of atoms
atomic structure of chlorine
class 11 chemistry chapter 4 notes
class 11 biology chapter 2 notes
ip class 11
atomic structure of calcium
o2 valence electrons
ncert solutions for class 11 chemistry chapter 2
nuclei class 12 notes
the nucleus of an atom is made up of
cbse online class 11
class 11 english chapter 2
atomic structure of nitrogen
ncert class 11 english
atomic structure of potassium
business studies class 11 chapter 1 notes
lewis dot diagram for oxygen
atomic structure of lithium
atomic structure of helium
no of atoms in hcp
nucleus of an atom consists of
class 11 biology notes chapter 1
class 11 chemistry notes pdf
human eye and colourful world notes
atomic structure of magnesium
class 9 science chapter 11
atomic structure model
information practices class 11
thermodynamics class 11 chemistry notes
exercise 1.4 class 11 maths
atoms of element b form hcp lattice
notes of business studies class 11 chapter 1
atomic theory was given by
class 11 physics chapter
class 11 physics chapter 3
class 11 english guide
nuclear structure
chapter 11 class 10 maths
s block elements ncert pdf
atomic structure and the periodic table
in an atom the nucleus contains
structure of atom class 11 ncert solutions
class 11 chapter 1
ncert class 11th
the first use of quantum theory to explain the structure of atom was made by
class 11 physics chapter 4 notes
chapter 5 class 11 maths
class 11 physics notes pdf
notes of class 11 chemistry chapter 1
chapter 11 science class 10
class 11 chemistry chapter 5 notes
ch 1 chemistry class 11 notes
chapter 2 chemistry class 11 notes
class 11 accountancy notes pdf
chapter 4 chemistry class 11
class 11 chemistry chapter 2 ncert solutions
chapter 3 class 11 maths
atomic structure of first 20 elements
class 11 physics chapter 5 notes
chemistry chapter 2 class 11 notes
class 11 physics notes chapter 1
atomic structure definition
accountancy class 11 chapter 1 notes
vedantu class 11 maths
chapter 1 class 11 maths
lithium has a bcc structure
chapter 10 class 11 maths
english core class 11
p block elements class 11 ncert pdf
electron dot structure of nitrogen molecule
cbse class 11 maths
structure of atom class 9 solutions
class 11 chemistry chapter 3
ncert solutions class 11 chemistry chapter 2
basic structure of an atom
electron orbit
class 10 science chapter 11 notes
class 11 biology chapter 3 notes
atomic structure ppt
ncert solutions for class 11 biology chapter 2
atomic structure diagram
successcds class 11 english
meritnation class 11
organic chemistry chapters of class 11
atomic structure of neon
structure of atom class 9 ppt
structure of atom class 11 solutions
chemistry atomic structure
structure of atom class 11 handwritten notes
the human eye and the colourful world notes
structure of atom class 11 ppt
no of atoms in fcc
describe the nucleus of an atom
ncert history class 11
class 11 maths ch 1
chapter 3 chemistry class 11 notes
environmental chemistry class 11 notes
structure of atom class 10
electronic structure of chlorine
nucleus of atom consists of
class 11 biology chapter 1 pdf
class 11 chemistry chapter 4 notes pdf download
chapter 3 physics class 11 notes
class 11 maths chapter 1 sets notes
ch 9 class 11 maths
atomic structure of boron
organic chemistry class 11 ncert solutions
chemistry class 11 chapter 1 notes pdf download
class 11 biology notes pdf for neet
atomic model of carbon
class 11 biology chapter 4 notes
class 11 biology chapter 1 the living world notes
class 11 maths ch 9
class 11 chemistry handwritten notes pdf in hindi
fluorine dot diagram
diamond atomic structure
thermodynamics class 11 physics notes
class 11 chemistry chapter 1 exercise
chapter 7 class 11 maths
an element having bcc structure
class 11 chemistry chapter 1 notes pdf download
class 11 chapter 1 chemistry notes
class 11 maths chapter
silicon atomic structure
states of matter class 11 pdf
preeti arora python class 11
class 11 maths ch 10
atomic structure of fluorine
physics wallah class 11 notes
class 11 chemistry chapter 4
ch 11 maths class 12
gold atomic structure
states of matter class 11 ncert pdf
chapter 1 class 11 chemistry
nuclei class 12
structure of atom ncert solutions
chapter 4 chemistry class 11 notes
octet rule lewis structure
electron dot diagram for oxygen
atomic structure of phosphorus
chapter 15 class 11 maths
a solid has a structure in which w atoms are located
class 11 physics chapter 4
class 11 physics chapter 6 notes
structure of atom class 11 notes study rankers
class 9 science ch 4
atomic structure of argon
class 12 maths chapter 11
chapter 2 class 11 maths
examfear class 11
atoms are the building blocks for
class 11 biology chapter 8 notes
atomic models in chemistry
topper notes class 11 chemistry
class 9 science chapter 11 notes
class 11 chemistry notes in hindi
ncert solutions for class 12 chemistry chapter 11
cbse class 11 physics
accountancy class 11 chapter 3 notes pdf
miscellaneous exercise chapter 11 class 12
class 11 biology chapter 5 notes
different atomic models
class 11 physics notes in hindi
atomic structure in hindi
chemistry class 11 chapter 4 notes
no of carbon atoms in diamond unit cell
class 11 chemistry chapter 6 notes
ncert solutions for class 11 physics chapter 4
11th chemistry notes
political science class 11 chapter 1 notes in hindi
nitrogen electron dot diagram
ncert class 11 chemistry chapter 1
class 11 physics notes chapter 2
atomic structure of iron
no of atoms in hcp unit cell
class 11 chemistry handwritten notes pdf download
class 11 chemistry chapter 7 notes
thermodynamics ncert pdf
class 9 chemistry chapter 4
atomic structure of beryllium
class 11 maths chapter list
class 12 chemistry chapter 11 ncert solutions
class 11 maths chapter 15
an element has bcc structure
class 11 maths chapter 12
s block elements class 11 ncert pdf
no of atoms in bcc
hydrocarbons class 11 ncert solutions
hydrogen chapter class 11
class 11 chapter 2 chemistry notes
class 11 physics chapter list
states of matter class 11 ncert solutions
rutherford atomic model class 9
carbon electron dot diagram
electron dot structure of water molecule
class 11 biology chapter 2
general organic chemistry class 11
class 11 maths chapter 1 notes
cbse schools near me for 11 and 12
an element x having fcc structure
inside the atom class 8
atoms and nuclei class 12
emerging modes of business class 11 notes
class 11 physics chapter 7 notes
chapter 1 business studies class 11
class 11 chemistry chapter
class 11 chemistry chapter 12 notes
atomic nucleus definition
bohr diagram for magnesium
class 11 chemistry notes pdf download
chapter 11 class 9 science
structure of atom class 9 ncert solutions
3d atomic model
class 11th political science
ncert class 9 science chapter 4
atomic model project
chapter 11 class 12 maths
mole concept class 11 notes
vedantu notes class 11
cbse class 11 chemistry
chemistry chapter 3 class 11 notes
the element having no neutron in the nucleus of its atom is
class 6 science chapter 11 notes
chemical bonding class 11 notes pdf
cbse results class 11
atomic structure of sulphur
physical education class 11th
chapter 5 chemistry class 11
chapter 11 class 11 maths
class 10 chapter 11
hydrocarbons class 11 pdf
cbse guide class 11
the correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is
in a solid ab having the nacl structure
ncert solutions for class 11 biology chapter 3
chemistry class 11 notes chapter 1
ch 6 class 11 maths
chapter 12 class 11 maths
class 11 physics chapter 4 ncert solutions
an element has a body centred cubic
ncert class 11 chemistry notes
cbse class 11 english
cbse class 11 physics notes
class 11 hydrogen notes
equilibrium class 11 ncert solutions pdf
class 11 equilibrium notes
class 11 chemistry chapter 2 solutions
class 11 physics chapter 10 notes
class 11 chemistry chapter 5 ncert solutions
define atomic structure
11th chemistry notes pdf download
class 11 physics chapter 9 notes
name the ketone having 4 carbon atoms and write its structure
class 11 english chapter 3
the s block elements class 11 notes
chapter 11 class 10 science
class 11 business studies notes pdf
lewis dot diagram for fluorine
class 11 maths ch 2
equilibrium class 11 notes pdf download
bst class 11 chapter 1 notes
class 11 physics chapter 5
chemistry class 11 guide pdf
chlorine electron dot diagram
notes of chapter 1 chemistry class 11
class 11 ch 10 maths
class 11 chemistry ncert solutions hindi medium
states of matter ncert pdf
thermodynamics class 11 chemistry notes for neet
bohr orbit
class 11 chemistry chapter 2 exercise solutions
organic chemistry chapters class 11
hydrogen chapter class 11 notes
ncert solutions for class 11 physics chapter 5
thermodynamics class 11 notes chemistry pdf download
class 11 biology ncert notes
electronic structure of fluorine
physics wallah notes class 11 physics
class 11 chemistry chapter 2 notes pdf
electron dot diagram for lithium
the nucleus of a hydrogen atom consists of
cbse 11
class 11 maths ch 7
nucleus in physics
class 11 chapter
cbse class 11 chemistry notes
octet structure
located in the nucleus of an atom
ncert class 11 maths chapter 1
chemistry notes for class 11 pdf free download in hindi
hydrocarbons class 11 notes pdf
class 11 chemistry chapter 12 ncert solutions
ncert solutions for class 11 chemistry chapter 5
atomic structure ncert
electron dot structure of sulphur molecule
class 11 chemistry chapter 8 notes
first atomic model
lithium metal has a body centred cubic structure
chapter 6 chemistry class 11 notes
class 11 physics chapter 2 notes pdf
python4csip class 11
notes of chapter 2 chemistry class 11
the nucleus of the atom consists of
class 11 biology chapter 7 notes
chapter 5 chemistry class 11 notes
states of matter class 11 notes pdf
atomic structure of elements
class 10 chapter 11 maths
class 9 science chapter 4 solutions
iupac nomenclature class 11 notes pdf
thermodynamics class 11 physics ncert solutions
no of atoms per unit cell in fcc
ch 2 class 11 maths
stoichiometry class 11 notes pdf
class 11 business studies notes pdf
physical education class 11th
cbse class 11 chemistry notes
ncert class 11 chemistry notes
class 11 biology ncert notes
cbse 11
cbse class 11 chemistry
class 11 physics chapter 2 notes pdf
cbse class 11 physics notes
notes of business studies class 11 chapter 1
class 11 physics notes in hindi
business studies class 11 chapter 1 notes
ncert exemplar class 11 physics
meritnation class 11
class 11th business studies chapter 1 notes
class 11th business studies notes
class 11 physics 1st chapter
class 11 physics chapter
class 11th bst notes
business studies poonam gandhi class 11
best notes for class 11 chemistry
ncert class 11 chemistry part 1
organic chemistry class 11 notes pdf
in a face centered lattice of x and y
ncert class 11 physics
class 11 chemistry notes
ncert class 11 physics part 2
physical education class 11th notes
ncert class 11 chemistry
class 11 chemistry chapter 1
class 11 chemistry chapter
class 11 biology notes
types of crystalline solid
metallic crystalline solid
ionic crystalline solid examples
ncert exemplar class 11 maths
ncert exemplar class 11 biology
english core class 11
notes of class 11 chemistry chapter 1
class 11 english chapter 1
class 11 physics best notes
class 11th notes
class 11 maths notes
ncert class 11 chemistry part 2
class 11 chemistry chapter 1 notes
class 11 chemistry
chemistry notes pdf class 11
cbse class 11 physics chapter 1 notes
ncert class 11 maths
class 11 physics notes pdf
class 11 english
ncert class 11th
class 11 physics
business studies class 11th
topper notes class 11 chemistry
class 11 maths chapter 1 sets notes
notes for class 11 english
ncert exemplar class 11 chemistry
class 11 chemistry notes pdf in hindi medium
class 11th science notes
class 11 chemistry notes pdf
ip class 11
class 11 maths
11th chemistry notes
class 11 biology ncert
class 11 chemistry notes pdf download
structure of atom
ncert history class 11
class 11 biology chapters
class 11 biology
the living world class 11th notes
class 11 biology notes chapter 1
successcds class 11 english
class 11th accountancy notes
class 11th computer science
class 11 maths guide
unacademy class 11 and 12
python fundamentals class 11
class 11 english guide
chemical bonding class 11 neet notes pdf
equilibrium class 11 notes for neet
legal studies class 11 cbse
free online classes for class 11 cbse
class 11 biology chapter 1 notes
class 11 physics by physics wallah
cbse class 11 notes
cbse class 11
class 11 biology chapter 1
class 11 physics notes
cbse class 11 computer science
structure of atom class 11 notes
class 11 accountancy notes pdf
best physics guide for class 11 cbse
atomic structure neet notes
best notes for class 11
class 11 vedantu
cbse economics class 11
accountancy class 11 chapter 1 notes
chapter 2 chemistry class 11 notes
informatics practices class 11
class 11 physics chapter 1 notes
information practices class 11
class 11 maths handwritten notes pdf
cbse class 11 schools near me
free online classes for class 11 cbse science
all in one class 11 english
states of matter class 11 notes for neet
vedantu class 11
ncert class 11 physics notes
class 11th physics guide
class 11 biology notes pdf
best online coaching for class 11 cbse
class 11 chemistry notes pdf free download
class 11 chemistry handwritten notes pdf
unacademy notes class 11
online coaching for class 11 cbse free
ncert class 11 english
chapter 3 chemistry class 11 notes
thermodynamics class 11 chemistry notes for neet
3d atomic model
class 11 biology neet notes
chemical bonding class 11 jee notes
class 11 chemistry handwritten notes pdf free download
best guide for class 11 cbse
applied math class 11
resonance notes for class 11 chemistry
class 11 business studies chapter 1
structure of atom class 9 notes byju's
class 11 chapter 1
cbse class 11 physics
equilibrium class 11 notes byju's
byju's class 11 notes
byju's class 11 physics solutions
byju's class 11 physics
structure of atom class 9 byju's
class 11 biology notes byju's
class 11 biology ch 1
applied mathematics cbse class 11
structure of atom class 11 byju's
byju's class 11 business studies notes
topperlearning class 11
byju's class 11 chemistry notes
byju's class 11 physics notes
class 11 chemistry chapter 2 notes byju's
class 11 physics notes byju's
class 11 biology chapter 1 notes byju's
the living world class 11 notes byju's
class 11 chemistry chapter 1 notes byju's
byju's class 11 biology notes
byju's class 11 biology chapter 1 notes
units and measurements class 11 notes byju's
hydrogen class 11 notes byju's
byju's class 11 maths notes
structure of atom byjus
byju's class 11 commerce notes
online coaching classes for class 11
motion in a straight line class 11 byju's
cbse class 11 maths
byju's class 11 maths
cbse class 11 english
organic chemistry class 11 byju's
cbse class 11 commerce
class 11 maths ch 1
states of matter class 11 notes byju's
chapter 1 physics class 11th notes
business studies class 11 chapter 1
class 11 maths chapter 1
vedantu class 11 english
vedantu notes class 11 physics
cbse 11 maths
chemistry class 11 neet notes pdf
akash notes for class 11 chemistry
p block elements class 11 neet notes
class 11 chemistry ch 1
basic principles of organic chemistry class 11 pdf
class 11 chemistry chapter 1 exercise
best notes for class 11 physics
aakash institute notes of physics class 11
hydrocarbons class 11 notes for neet
class 11 physics chapter 1
class 11 chemistry chapter 1 notes unacademy
cbse 11 and 12 schools near me
study material for class 11 chemistry
class 11 chemistry chapter 2
nucleus in physics
computer science class 11 python
organic chemistry class 11 notes
organic chemistry pdf class 11
byju's notes class 11 pdf
atomic structure notes for neet
chemistry class 11 jee notes
notes of class 11 physics chapter 1
cbse biology class 11
structure of atom class 11
cbse class 11 notes pdf
cbse schools for 11th and 12th near me
class 11 physics notes chapter 1
class 11 physics chapter 1 notes unacademy
vedantu class 11 physics
organic chemistry class 11 notes for neet
states of matter class 11
structure of atom class 9 notes
class 11 chemistry chapter 2 notes
states of matter class 11 notes
class 11 physics chapter 2 notes
chemical bonding class 11 notes
redox reaction class 11 notes
atomic structure notes
nucleus of an atom contains
fluorine lewis dot structure
describe the structure of an atom
thermodynamics class 11 notes
atomic structure of oxygen
class 9 science chapter 4
p block elements class 11
atomic structure of sodium
class 11 chemistry chapter 3 notes
mycbseguide class 11
atomic structure of hydrogen
atomic structure of carbon
structure of water molecule
electron dot structure of chlorine
hydrocarbons class 11 notes
ccp lattice
ncert solutions for class 9 science chapter 4
ch 11 maths class 10
equilibrium class 11 notes
thermodynamics class 11 chemistry
my cbse guide class 11
class 11 maths chapter 9
class 11 physics chapter 3 notes
hydrogen class 11 notes
chapter 2 chemistry class 11
class 11 maths chapter 10
s block elements class 11 notes
rutherford model of atom class 11
class 11 maths chapter 2
electronic structure of sodium
p block elements class 11 notes
in a solid ab having nacl structure
electronic structure of atoms
atomic structure of chlorine
class 11 chemistry chapter 4 notes
class 11 biology chapter 2 notes
atomic structure of calcium
o2 valence electrons
ncert solutions for class 11 chemistry chapter 2
nuclei class 12 notes
the nucleus of an atom is made up of
class 11 english chapter 2
atomic structure of nitrogen
atomic structure of potassium
lewis dot diagram for oxygen
atomic structure of lithium
atomic structure of helium
no of atoms in hcp
nucleus of an atom consists of
human eye and colourful world notes
atomic structure of magnesium
class 9 science chapter 11
atomic structure model
thermodynamics class 11 chemistry notes
exercise 1.4 class 11 maths
atoms of element b form hcp lattice
atomic theory was given by
class 11 physics chapter 3
nuclear structure
chapter 11 class 10 maths
s block elements ncert pdf
atomic structure and the periodic table
in an atom the nucleus contains
structure of atom class 11 ncert solutions
the first use of quantum theory to explain the structure of atom was made by
class 11 physics chapter 4 notes
chapter 5 class 11 maths
chapter 11 science class 10
class 11 chemistry chapter 5 notes
ch 1 chemistry class 11 notes
chapter 4 chemistry class 11
class 11 chemistry chapter 2 ncert solutions
chapter 3 class 11 maths
atomic structure of first 20 elements
class 11 physics chapter 5 notes
chemistry chapter 2 class 11 notes
atomic structure definition
chapter 1 class 11 maths
lithium has a bcc structure
chapter 10 class 11 maths
p block elements class 11 ncert pdf
electron dot structure of nitrogen molecule
structure of atom class 9 solutions
class 11 chemistry chapter 3
ncert solutions class 11 chemistry chapter 2
basic structure of an atom
electron orbit
class 10 science chapter 11 notes
class 11 biology chapter 3 notes
atomic structure ppt
ncert solutions for class 11 biology chapter 2
atomic structure diagram









No comments:
Post a Comment